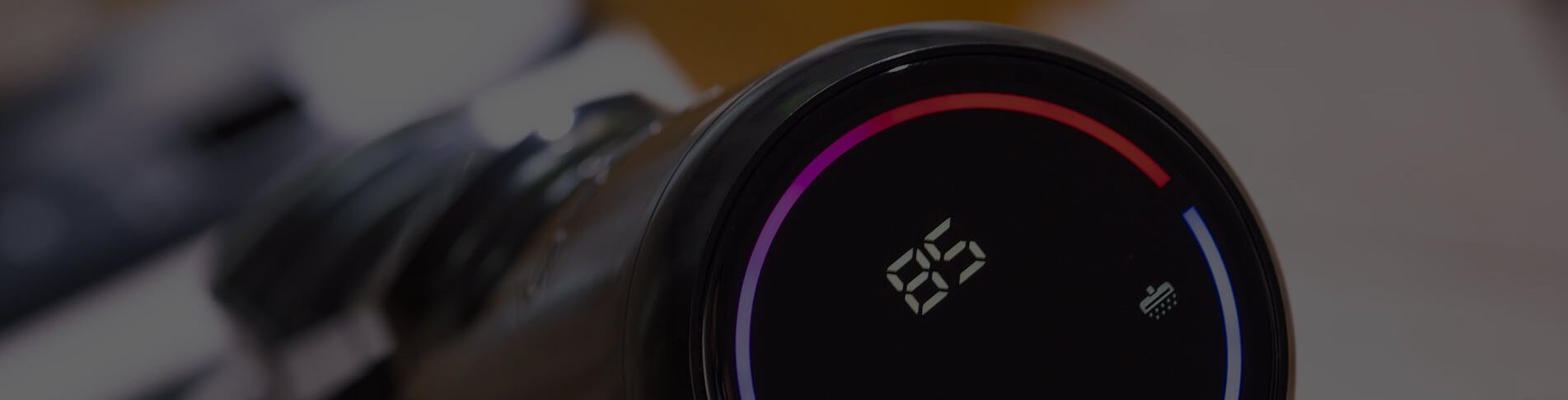
The difference between TFT LCD, OLED and Micro LED part two
Jun 11, 2024
OLED
Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) refers to the phenomenon in which organic semiconductor materials and luminescent materials emit light through carrier injection and recombination when driven by an electric field. Under the action of the electric field in OLED, the holes generated by the anode and the electrons generated by the cathode will move, inject into the hole transport layer and electron transport layer respectively, and migrate to the light-emitting layer. When the two meet in the light-emitting layer, they generate energy excitons, which excite the light-emitting molecules and ultimately produce visible light.
[Advantage]
Each pixel of the OLED screen is self-illuminating, so it is thinner and lighter than LCD;
Low power consumption and flexibility: Compared with LCD, OLED saves structures such as backlights, liquid crystals and color filters, has lower power consumption, and can achieve flexible display;
High contrast, high brightness, high luminous efficiency, and more vivid image colors: OLED is self-luminous and can not emit light at all when necessary, displaying more pure black;
The unit response speed of OLED screen is faster than that of LCD screen.
[Disadvantage]
OLED screens are prone to screen burn-in;
The lifespan of blue OLED is relatively short;
The stroboscopic phenomenon is obvious, the colors are bright and there is a color cast problem, and long-term use will cause harm to the eyes;
The pixel density is low, and the display effect is not as good as LCD display effect at the same resolution.






 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch русский
русский español
español العربية
العربية


 IPv6 network supported
IPv6 network supported
