Brief ntroduction of OLED structure and light-emitting principle part one
Mar 24, 2023
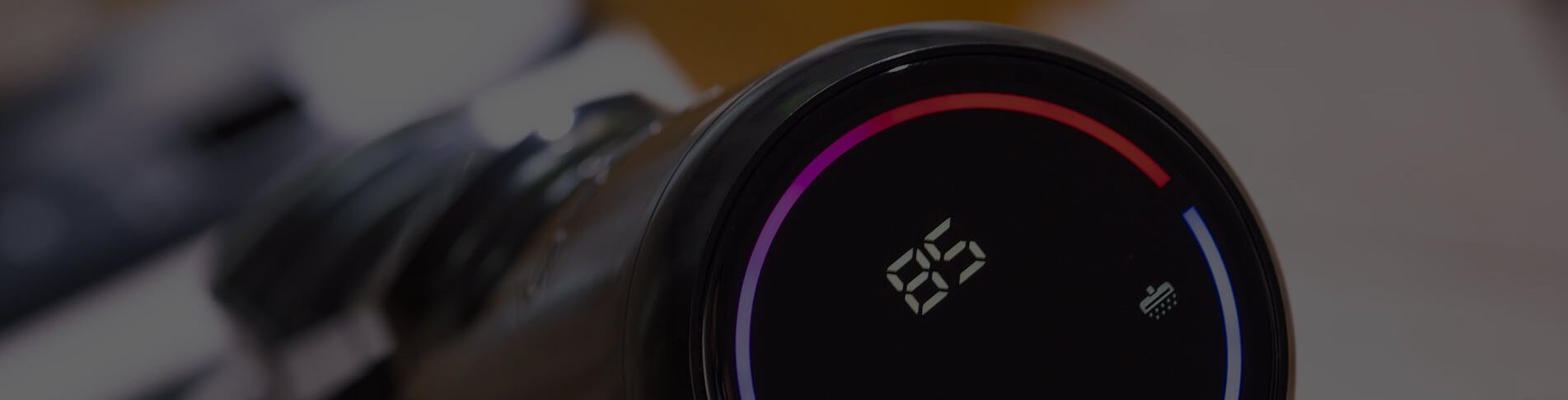
The original text of OLED is Organic Light Emitting Diode, which means "organic light-emitting display technology" in Chinese. The principle is that an organic light-emitting layer is sandwiched between two electrodes. When the positive and negative electrons meet in this organic material, it will emit light. Its component structure is simpler than the current popular TFT LCD, and the production cost is only three to four of the TFT LCD. into about. In addition to the cheap production cost, OLED module has many advantages, such as its own light-emitting characteristics. Currently, LCD requires a backlight module (a lamp is added behind the liquid crystal), but OLED will emit light by itself after it is powered on, which can save the weight of the lamp. Volume and power consumption (the power consumption of the lamp tube accounts for almost half of the entire LCD screen), not only the thickness of the product is only about two centimeters, the operating voltage is as low as 2 to 10 volts, plus the response time of the OLED (less than 10ms) And the color is better than TFT LCD, more flexible characteristics, it has a wide range of applications.
OLED structure and light-emitting principle
The basic structure of OLED is to make a layer of organic light-emitting material with a thickness of tens of nanometers on indium tin oxide (ITO) glass as the light-emitting layer, and there is a layer of metal electrodes with low work function above the light-emitting layer to form a sandwich-like structure.
The basic structure of OLED mainly includes:
Substrate (clear plastic, glass, metal foil) - The base layer is used to support the entire OLED.
Anode (Transparent) - The anode eliminates electrons (adds electron "holes") when current flows through the device.
Hole Transport Layer - This layer consists of molecules of organic material that transport the "holes" from the anode.
Light Emitting Layer - This layer is composed of molecules of organic material (different from the conductive layer) where light emission takes place.
Electron Transport Layer - This layer consists of molecules of organic material that transport "electrons" from the cathode.


 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch русский
русский español
español العربية
العربية


 IPv6 network supported
IPv6 network supported
