1. Introduction to TFT
TFT is the abbreviation of the English initials of Thin Film Transistor. It has the dual characteristics of "active (switching, amplification)" of a transistor and "thin" of a "thin film". It is combined with a flat-panel display screen (such as LCD, OLED, etc.) to form today's flat-panel TV (TFT-LCD, TFT -OLED), TFT is one of the key core components.
Usually the active material of TFT is silicon film. According to the different structure of silicon film, transistors are divided into amorphous silicon TFT (a-Si TFT), polycrystalline silicon (p-Si TFT) and single crystal silicon MOSFET (c-Si MOSFET). In addition, TFTs made of organic materials are called organic TFTs (or OTFTs).
Since its invention in the 1960s, thin film transistors have been widely promoted and applied, and their development speed is beyond imagination. From amorphous silicon TFT to polycrystalline silicon TFT, from high-temperature polycrystalline silicon TFT to low-temperature polycrystalline silicon TFT, the technology is becoming more and more mature, and the application object has also developed from just driving LCD to driving LCD, OLED, and even electronic paper. As the level of semiconductor technology continues to improve, the pixel size continues to decrease, and the resolution of the display screen becomes higher and higher.
TFT-addressed LCD displays have become the dominant technology for LCDs and even flat panel displays with their large capacity, high definition and full-color video display, and related high-tech industries have also become the current main investment direction. TFT manufacturing technology plays a key role in TFT-addressed liquid crystal displays, and its research and development has always been the focus of research.
2. Display driving method
Both LCD and OLED displays are divided into two categories: active display and passive display. For LCD display, it is divided into passive (passive) drive display LCD, such as: Color-STN-LCD display, STN-LCD, TN-LCD, etc.; active (active) drive display LCD, such as: TFT-LCD. For OLED display, it is divided into passive (passive) drive display OLED (PMOLED) and active (active) drive display OLED (AMOLED).
Passive (passive) drive display OLED or LCD can usually only display less than 200 lines at the same time. Therefore, to display more lines to achieve high definition, an active (active) drive display method is used, that is, TFT-LCD, AMOLED. Active (active) drive display methods include TFT production technology.
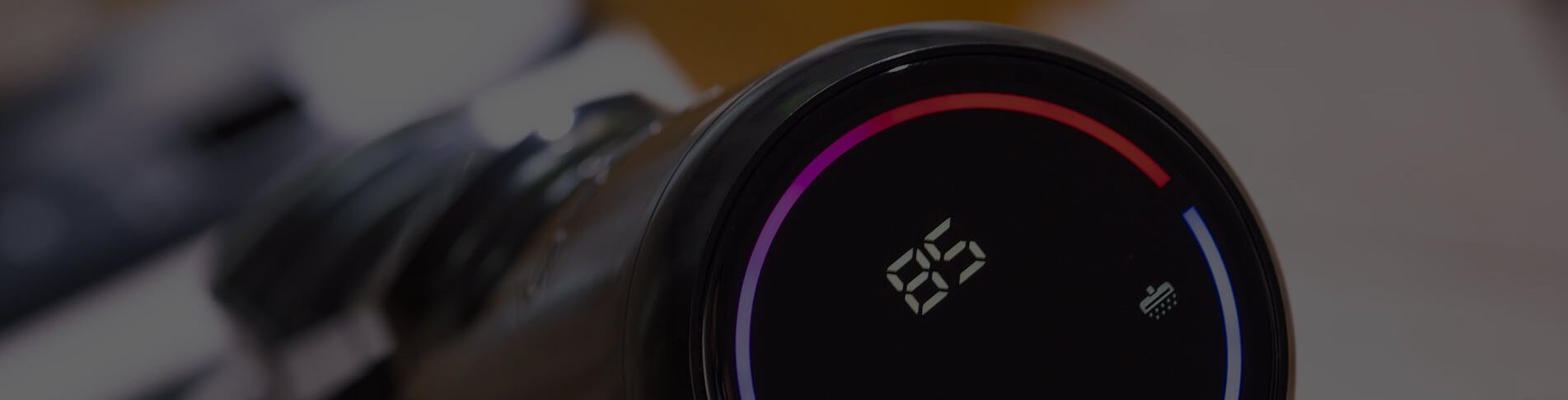
3. TFT film technology
1. Amorphous silicon film. Amorphous silicon thin film transistor technology was proposed in the 1970s. After nearly 30 years of unremitting efforts by scientists from various countries, now all seventh-generation liquid crystal display (LCD) production lines have been automated, and industrial production technology is quite mature. It has developed into the mainstream product of LCD monitors in the world today, and the goal of future development is larger screen size and lower production cost. The advantage of amorphous silicon TFT technology is that the preparation process is mature, relatively simple, and has a high yield, making it suitable for large-area production. The disadvantage is that TFT only has N-type devices and its mobility is only 0.5-1.0cm2/Vs. Therefore, it is difficult to prepare high-performance, fully integrated, ultra-thin and compact display modules using the amorphous silicon TFT process. Amorphous silicon TFT technology cannot be used for high-resolution active-driven OLED displays.
2. Polycrystalline silicon film (poly-Si). Polycrystalline silicon thin film processes are mainly divided into two categories:
(1) High-temperature process refers to the temperature being higher than 900°C during the entire processing process. The high-temperature process can only use expensive quartz as the substrate, and the TFT performance is good. The high-temperature process is only suitable for small and medium-sized display screens or projection screen series.
(2) Low-temperature process, the temperature during the entire processing process is lower than 600°C. Larger displays can be made on cheap glass substrates using low-temperature processes. Low-temperature polysilicon (LTPS) TFTs are widely used in active (active) drive display TFTs-LCDs and AMOLEDs due to their low power consumption, lightness, thinness, large current supply and system integration. The key to the polycrystalline silicon TFT process is how to prepare high-quality polycrystalline silicon thin films in a large area at low cost. Currently, methods for preparing polysilicon materials include rapid annealing (RTA), excimer laser crystallization (ELC), solid phase crystallization (SPC), continuous lateral crystallization (SLS) and metal-induced low-temperature polysilicon (MIC) technology.
Low-temperature polysilicon LTPS TFT technology can completely solve the problems that amorphous silicon TFT technology cannot solve. Especially after 2000, due to the overcapacity of a-Si TFT, Japanese, Korean and Taiwanese manufacturers actively invested in LTPS TFT, giving LTPS TFT more development opportunities in the next few years. Especially with the recent rapid growth of the small and medium-sized panel market, the development of polysilicon TFT has begun to enter a golden period. LTPS TFT has long been regarded as a necessary technology for the next generation of LCD.
3. Organic thin film TFT. It is self-evident that the emergence of organic TFTs will form strong competition for existing amorphous silicon TFTs. It will be the core technology of a new generation of flexible displays. Displays made using flexible display technology can be rolled like a canvas and may become an important player in the future display world like LCDs.
Due to the use of organic materials, it has the characteristics of a flexible display, so it is not only impact-resistant, but also lightweight and small in size. Not only has the appearance of the display been changed, but the application environment has also been greatly expanded and diversified. Printing displays on plastic film sheets using a tape-and-reel process similar to the newspaper printing process can greatly reduce production costs.
OTFT research has been carried out internationally for nearly 20 years, but how to design and process high-performance devices, how to reduce processing costs, and how to synthesize organic semiconductor materials with both high mobility and environmental stability have always been research and technical bottlenecks. At present, No substantial breakthrough has been achieved yet. On the whole, international research in the field of flexible electronics is still in its infancy, and there is huge room for technological breakthroughs and patent applications.
4. Applications of TFT displays (mainly the following four categories)
1. Portable display: video-capable mobile phone, video-capable PDA, video-capable e-book, etc.;
2. Vehicle-mounted display: GPS, safe driving display, multimedia display, etc.;
3. Computer display: laptop, monitor, etc.;
4. Home appliances and office displays: TVs, Internet terminals, electronic newspapers, etc.
In short, TFT technology occupies a core position in the flat panel display industry. It is capital-intensive, talent-intensive, and technology-intensive. The panel output value is high and the industry agglomeration effect is obvious.






 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch русский
русский español
español العربية
العربية


 IPv6 network supported
IPv6 network supported
